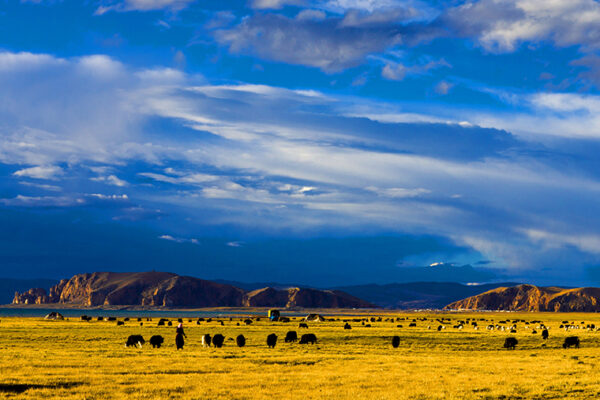
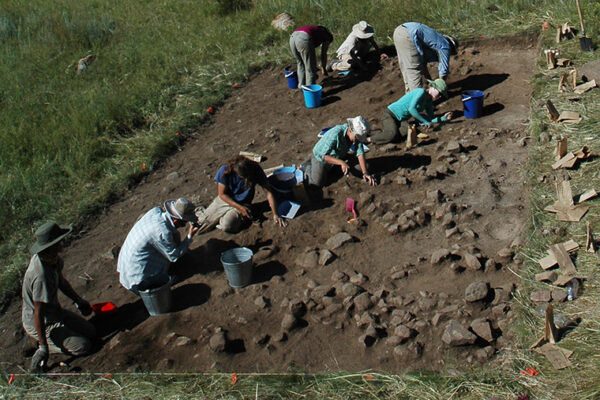
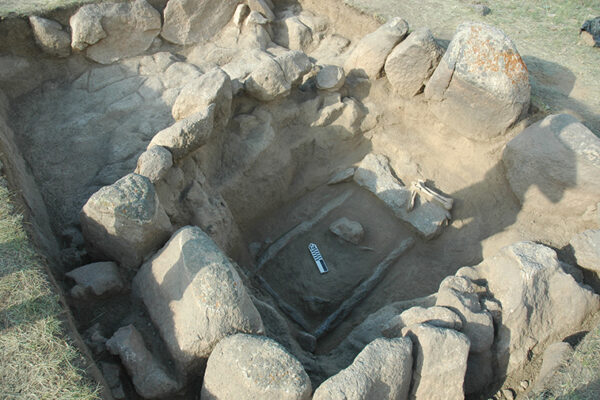
The main focus of Frachetti’s research is on the dynamic strategies of pastoral nomadic societies living in the steppe region, mountains and deserts of Central and Eastern Eurasia. His work centers primarily on pastoralism in the Bronze Age (~3500-1000BC), which is intricately tied to questions of social and economic interaction between regional populations across Central Asia at that time. His theoretical interests center on how social groups utilize economic and political strategies to communicate inter-regionally, and how variability in their economic and social strategies introduces opportunities for reshaping the boundaries of their social landscapes and human interactions.

Michael Frachetti
Professor of Archaeology
Contact Information
- Phone: 314-935-5870
- Email: frachetti@wustl.edu
- Website: Website
Media Contact
In the media
Oldest evidence of marijuana use discovered in 2500-year-old cemetery in peaks of western China
Michael Frachetti, professor of archaeology
Ancient drug paraphernalia reveals that people smoked pot in China 2,500 years ago
Michael Frachetti, professor of archaeology
Silk Road nomads were the original foodies
Michael Frachetti, associate professor of archaeology
Stories
Prehistoric mobility among Tibetan farmers, herders shaped highland settlement patterns, cultural interaction, study finds
Research by Michael Frachetti in Arts & Sciences and researchers at Sichuan University in China explores how and why ancient communities built social relationships and cultural identities across the extreme terrain in Tibet.
New tool to enable exploration of human-environment interactions
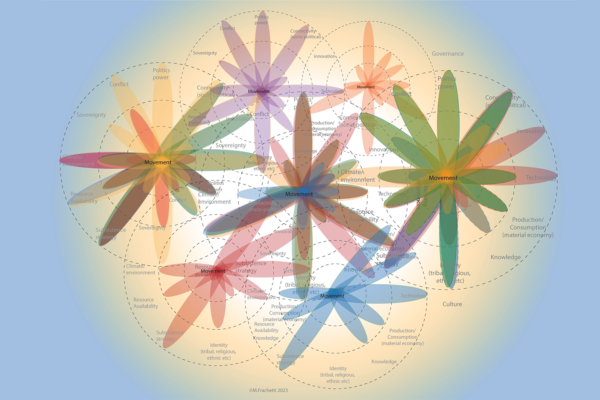
In a new Science Advances report, a team of researchers led by Michael Frachetti in Arts & Sciences is calling for a strengthened commitment to transdisciplinary collaboration to study past and present human-environmental interactions, which they say will advance our understanding of the complex, entangled histories.
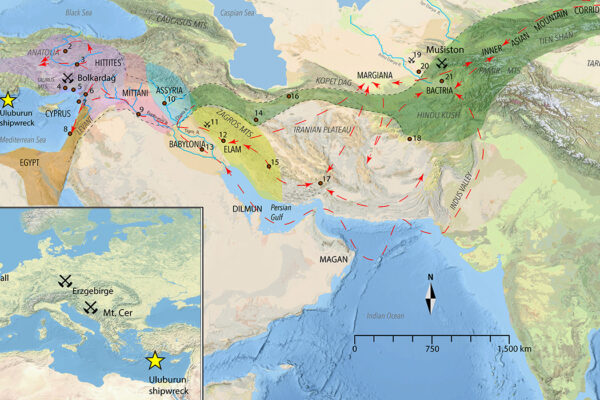
Findings from 3,000-year-old Uluburun shipwreck reveal complex trade network
Using advanced geochemical analyses, a team of scientists, including Michael Frachetti, professor of archaeology in Arts & Sciences, have uncovered new answers to decades-old questions about trade of tin throughout Eurasia during the Late Bronze Age.
What the future holds for Ukraine, Kazakhstan
With decades of combined experience in Ukraine and Kazakhstan, Washington University social anthropologists Michael Frachetti and James V. Wertsch share their perspectives on the future of these countries following unrest.
Researchers of ancient DNA set guidelines for their work
Michael Frachetti, professor of archaeology in Arts & Sciences, participated in a global initiative that set best practices for ethically sampling human remains and carrying out scientific analysis. He says this type of collaboration across regional and disciplinary boundaries likely will shape the future of scholarly work.
Ancient DNA study tracks formation of populations across Central Asia
Ethically sourced and informed by archaeology, an ambitious new study reports genome-wide DNA information from 523 ancient humans collected at archaeological sites across the Near East and Central and South Asia. Washington University in St. Louis brought key partners together to generate the world’s largest study of ancient DNA, published this week in the journal Science.
Food culture along the Silk Road
Like passionate foodies who know the best places to eat in every town, Silk Road nomads may have been the gastronomic elites of the Medieval Ages, enjoying diets much more diverse than their sedentary urban counterparts, suggests a new study in Scientific Reports.
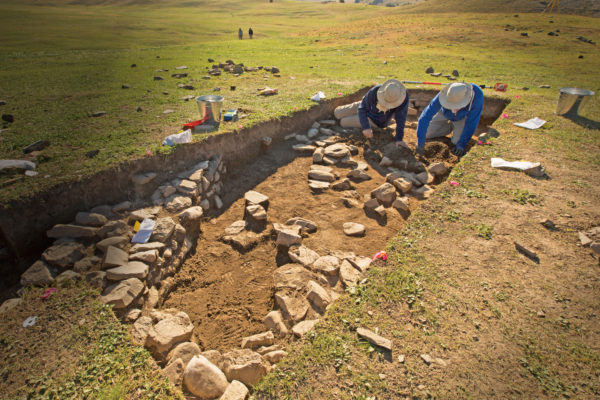
Targeted excavating leads to lost city
Using modern, high-tech analysis tools, anthropologist Michael Frachetti is leading groundbreaking research on an ancient city high in the Uzbekistan mountains. The site may hold clues to how medieval civilizations changed when diverse communities integrated — and even suggest how we might consider our own current initiatives of global community-building.
Digging Kazakhstan’s past helps students find themselves
Much more than an archaeology course, a six-week
summer field practicum on the history of Central Asia, led by Michael Frachetti, PhD, associate professor of archaeology in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, offers students
from all disciplines the opportunity to immerse themselves in the past and present culture of Kazakhstan.
Ancient nomads spread earliest domestic grains along Silk Road, study finds
Charred grains of barley, millet and wheat deposited nearly 5,000 years ago at campsites in the high plains of Kazakhstan show that nomadic sheepherders played a surprisingly important role in the early spread of domesticated crops throughout a mountainous east-west corridor along the historic Silk Road, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.